Department of Nephrology
Nephrology (from Greek nephros “kidney”, combined with suffix –logy, “the study of”) is a specialty of adult internal medicine and pediatric medicine that concerns the study of the kidneys, specifically normal kidney function (renal physiology) and kidney disease (renal pathophysiology), the preservation of kidney disease, from diet and medication to renal replacement therapy (dialysis and kidney transplantation).
Nephrology also studies systemic conditions that affects the kidneys, such as diabetes and autoimmune disease; and systemic diseases that occur as a result of kidney disease, such as renal osteodystrophy and hypertension. A physician who has undertaken additional training and become certified in nephrology is called a nephrologist.
The term “nephrology” was first used in about 1960, according to the French “nephrologie” proposed by Pr. Jean Hamburger in 1953. Before then, the specialty was usually referred to as “kidney medicine”.
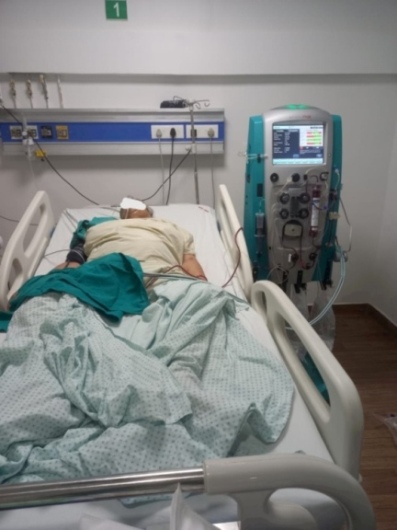
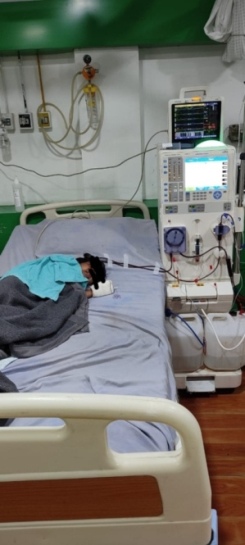
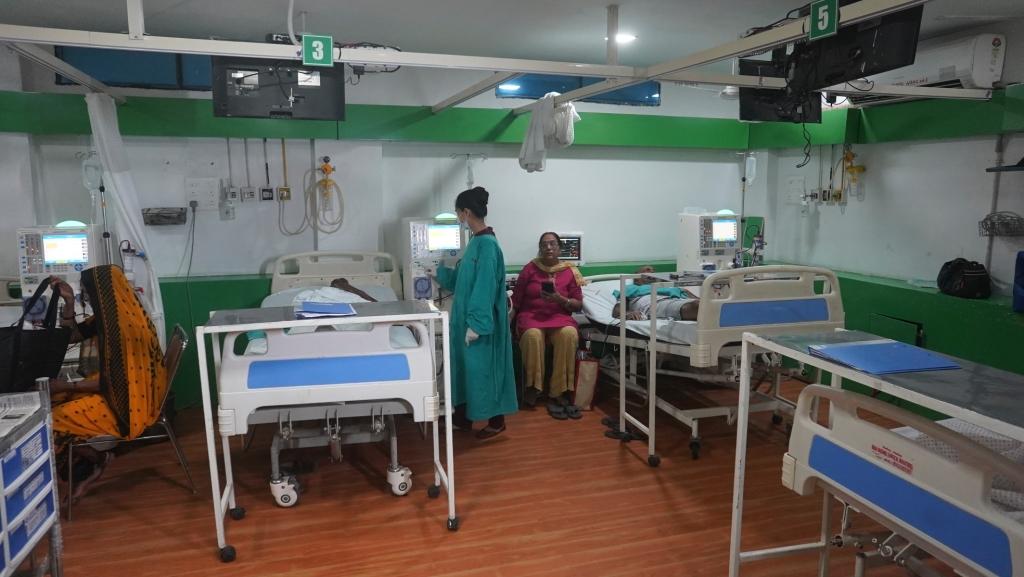
Nephrology concerns the diagnosis and treatment of kidney disease, including electrolyte disturbances and hypertension, and the care of those requiring renal replacement therapy, including dialysis and renal transplant patients. The word ‘dialysis’ is from the mid 19th century: via Latin from the Greek word ‘dialusis’; from ‘dialuein’ (split, separate), from ‘dia’ (apart) and ‘luein’ (set free). In other words, dialysis replaces the primary (excretory) function of the kidney, which separates (and removes) excess toxins and water from the blood, placing them in the urine.
Many diseases affecting the kidney are systemic disorders not limited to the organ itself, and may require special treatment. Examples include acquired conditions such as systemic vaculitides (e.g. ANCA vasculitis) and autoimmune diseases (e.g., lupus), as well as congenital or genetic conditions such as polycystic kidney disease.
Patients are referred to nephrology specialists after a urinalysis, for various resons, such as acute kidney injury, chronic kidney disease, hematuria, proteinuria, kidney stones, hypertension, and disorders of acid/base or electrolytes.
Nephrologist
A nephrologist is a physician who specializes in the care and treatment of kidney disease. Nephrology requires additional training to become an expert with advanced skills. Nephrologists may provide care to people without kidney problems and may work in general/internal medicine, transplant medicine, immunosupression management, intensive care medicine, clinical pharmacology, perioperative medicine, or pediatric nephrology.
Nephrologists may further sub-specialise in dialysis, kidney transplantation, chronic kidney disease, cancer-related kidney diseases (Onconephrology), procedural nephrology or other non-nephrology areas as described above.
Procedures a nephrologists may perform include native kidney and transplant kidney biopsy, dialysisaccess insertion (temporary vascular access lines, tunneled vascular access lines, peritoneal dialysis access lines) or fistula management (angiographic or surgical fistulogram and plasty).